Configuring BGP MED
Contents
Intro
Attributes like Weight and Local Preference influence outbound path selection of your AS. If you want to influence how traffic enters your AS then you can AS path prepending or Multi Exit Discriminator (MED). MED also referred to as “Metric” is a BGP attribute that’s used to hint or suggest to an external AS a preferred path they should use to reach your AS where the prefix that has the MED attached is coming from. When it comes to MED the lowest value is preferred.
MED is considered a weak attribute in the BGP Best Path Selection algorithm. This is because attributes like Weight, Local Preference, AS-Path and Origin are all looked at before MED.
Assume AS123 is your AS. I’ll show you how to configure MED so that you control how R4 (an external neighboring AS) enters your AS123 to reach 2.2.2.2/32.
Topology
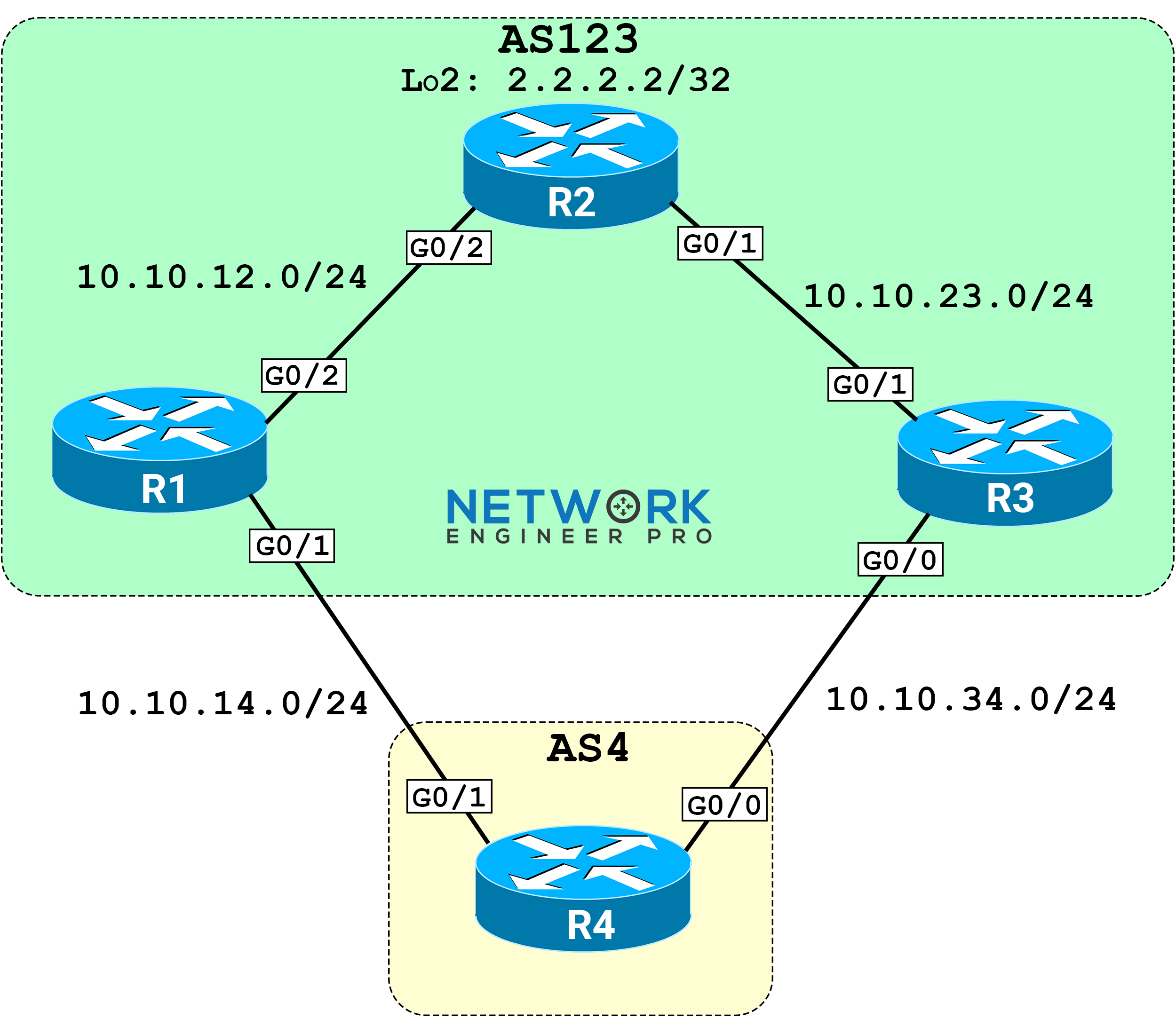
Initial Configs
conf t
host R1
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shut
ip address 10.10.14.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no shut
ip address 10.10.12.1 255.255.255.0
conf t
host R2
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface Loopback2
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shut
ip address 10.10.23.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no shut
ip address 10.10.12.2 255.255.255.0
conf t
host R3
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.34.3 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 10.10.23.3 255.255.255.0
no shut
conf t
host R4
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.34.4 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 10.10.14.4 255.255.255.0
no shut
Configuration Steps
1. Configure Basic BGP
The first thing I’ll do is get all the BGP peerings up and R2’s Lo2 prefix advertised into BGP.
R1:
router bgp 123
neighbor 10.10.12.2 remote-as 123
neighbor 10.10.14.4 remote-as 4
R2:
router bgp 123
neighbor 10.10.12.1 remote-as 123
neighbor 10.10.23.3 remote-as 123
network 2.2.2.2 mask 255.255.255.255
R3:
router bgp 123
neighbor 10.10.34.4 remote-as 4
neighbor 10.10.23.2 remote-as 123
R4:
router bgp 4
neighbor 10.10.34.3 remote-as 123
neighbor 10.10.14.1 remote-as 123 A few seconds later I get notified the neighbors are up.
R1:
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.12.2 Up
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.14.4 Up R2:
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.12.1 Up
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.23.3 Up R3:
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.23.2 Up
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.34.4 Up R4:
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.34.3 Up
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.14.1 Up Let me check the BGP table on R4.
R4#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 2, local router ID is 10.10.34.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 2.2.2.2/32 10.10.34.3 0 123 i
*> 10.10.14.1 0 123 i R4 is prefering the path via R1 to reach the 2.2.2.2/32 prefix. This is because at the moment, all attributes are tied so BGP will prefer the path that was received first (the oldest one) as it seems more stable. I’ll prove this really quick by shutting the connection on R4 towards R1. I’ll bring it back up and check the BGP table again.
R4:
int g0/1
shutdown R4:
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.14.1 Down Interface flap R4:
int g0/1
no shutdown R4:
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.10.14.1 Up R4#show ip bgp BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 10.10.34.4 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, t secondary path, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * 2.2.2.2/32 10.10.14.1 0 123 i *> 10.10.34.3 0 123 i
After bouncing the port R4 uses to connect to R1, the BGP peering went down and came back up. The BGP table on R4 shows the path via R3 is now the best path because the other attributes are tied up to the point that both paths are external, so BGP prefers the path that was received first (the oldest one).
What I’ll do now is make R4 always prefer the path via R1. I’ll do this from AS123 by going to R3 and configuring a really high (worse) MED value when it sends prefixes outbound to R4. Then I’ll configure a lower (more preferred) MED value on R1 as it sends prefixes outbound to R4.
R4 will see both paths and it will prefer the path with the lowest MED. That’s how I will control inbound traffic to AS123.
2. Configure BGP MED.
The first thing I need to do is to configure a route-map on R3.
R3:
route-map SET_MED permit 10
set metric 100
The route-map above sets the MED or metric to 100. This by itself won’t do anything until I apply the route-map to a neighbor.
R3:
router bgp 123
neighbor 10.10.34.4 route-map SET_MED out
The effect of this route-map is that R3 will attach a MED value of 100 to all prefixes sent outbound to R4. Now I’ll jump to R1.
R1:
route-map SET_MED permit 10
set metric 50
The route-map above sets the MED or metric to 50. This by itself won’t do anything until I apply the route-map to a neighbor.
R1:
router bgp 123
neighbor 10.10.14.4 route-map SET_MED out
The effect of this route-map is that R1 will attach a MED value of 50 to all prefixes sent outbound to R4. Now I’ll jump to R4.
From R4 I’ll check it’s BGP table.
R4#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 10.10.34.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 2.2.2.2/32 10.10.14.1 50 0 123 i
* 10.10.34.3 100 0 123 i
You can see in the about output that R4’s BGP table is showing the new MED values. The path via R3 has a MED of 100 and the path via R1 has a MED or metric of 50. When it comes to MED the lower values are preferred. Which is why the path via R1 is best. You can also see the MED values by looking at the details of the prefix.
R4#show ip bgp 2.2.2.2
BGP routing table entry for 2.2.2.2/32, version 5
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table default)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 2
123
10.10.14.1 from 10.10.14.1 (10.10.14.1)
Origin IGP, metric 50, localpref 100, valid, external, best
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Refresh Epoch 2
123
10.10.34.3 from 10.10.34.3 (10.10.34.3)
Origin IGP, metric 100, localpref 100, valid, external
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0
The details of the 2.2.2.2/32 prefix show the MED value of 50 from R1. It also shows the MED value of 100 from R3.
That’s it for this MED tutorial. Make sure you download the EVE-NG topology file so you can lab it out yourself. If you have any questions please let me know.
EVE-NG Lab File
Here’s the EVE-NG Topology file if you want to import it into your own EVE-NG lab and practice. Please note this is the topology file not the Cisco images, we don’t provide those.
Full Configs
Here are the full configs from all routers if you want to try it out yourself.
conf t
host R1
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shut
ip address 10.10.14.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no shut
ip address 10.10.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 123
neighbor 10.10.12.2 remote-as 123
neighbor 10.10.14.4 remote-as 4
neighbor 10.10.14.4 route-map SET_MED out
!
route-map SET_MED permit 10
set metric 50
conf t
host R2
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface Loopback2
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no shut
ip address 10.10.23.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no shut
ip address 10.10.12.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 123
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 2.2.2.2 mask 255.255.255.255
neighbor 10.10.12.1 remote-as 123
neighbor 10.10.23.3 remote-as 123
conf t
host R3
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.34.3 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 10.10.23.3 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
router bgp 123
neighbor 10.10.23.2 remote-as 123
neighbor 10.10.34.4 remote-as 4
neighbor 10.10.34.4 route-map SET_MED out
!
route-map SET_MED permit 10
set metric 100
conf t
host R4
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logg syn
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.34.4 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 10.10.14.4 255.255.255.0
no shut
!
router bgp 4
neighbor 10.10.14.1 remote-as 123
neighbor 10.10.34.3 remote-as 123
