BGP Next-Hop-Self
Contents
Images used in lab: VIOS-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.9(3)M2
Topology Interfaces Only
Topology With IP Addressing
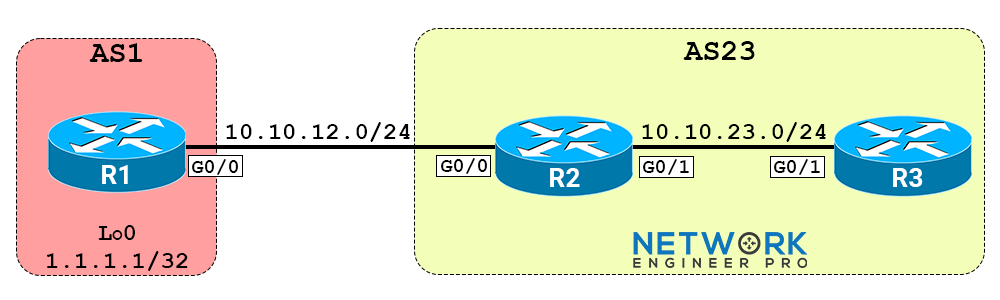
The last octet is the router number unless specified otherwise. Example: R1's G0/0 is 10.10.12.1/24. Access to the initial configs, EVE-NG lab file and solution is below.
Intro
By default, BGP updates sent to iBGP peers don’t modify the next-hop. This can cause problems if a router doesn’t know how to reach that next hop. If the recursive lookup for the next hop fails the prefix will not be considered for best path selection and will never make it to the routing table. In this lab you’ll see this problem from R3’s perspective and fix it using the BGP next-hop-self feature
Tasks
- Configure iBGP peerings between R2 and R3.
- Configure eBGP Peerings between R1 and R2.
- Use their directly connected links to establish all peerings.
- On R1, advertise its Loopback 0 prefix into BGP.
- On R2, advertise the 10.10.23.0/24 prefix into BGP.
- Use the next-hop-self command as needed to ensure full reachability between R3 and R1's Loopback 0.
Download Lab
To download the EVE-NG topology file you'll need to be a member. You can register here, It will be right here once you log in.
Initial Configs
R1
R2
R3
R1
conf t
hostname R1
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logging syn
!
int g0/0
no sh
ip add 10.10.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
int lo0
ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255R2
conf t
hostname R2
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logging syn
!
int g0/0
no sh
ip add 10.10.12.2 255.255.255.0
!
int g0/1
no sh
ip add 10.10.23.2 255.255.255.0
R3
conf t
hostname R3
no ip domain-lookup
line con 0
logging syn
!
int g0/1
no sh
ip add 10.10.23.3 255.255.255.0
Solution
Hope you enjoyed this lab. If you have questions or need any help at all please leave a comment below and I’ll get back to you.
